Saudi Arabia is undergoing a significant transformation, aiming to diversify its economy and promote sustainable development. Central to this endeavor is the integration of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors into financial risk assessments, aligning with global trends and the Kingdom’s Vision 2030 objectives. This article explores the evolution of ESG reporting and disclosure in Saudi Arabia, the significance of ESG integration in risk assessments, and the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
The Evolution of ESG Reporting and Disclosure in Saudi Arabia
Sustainable finance refers to financial services that consider ESG criteria to promote long-term economic growth and environmental stewardship. In Saudi Arabia, the concept has gained momentum, particularly after the announcement of Vision 2030, which aims to reduce the Kingdom’s dependence on oil and foster a more diversified and sustainable economy.
1.1 Vision 2030 and Sustainability and ESG Advisory
Vision 2030 outlines several initiatives to enhance sustainability, including the development of renewable energy projects, environmental conservation efforts, and social reforms. The integration of ESG factors into financial practices is seen as a critical component in achieving these goals. For instance, the Saudi Stock Exchange (Tadawul) has issued ESG advisory Guidelines to encourage listed companies to report on their ESG performance, thereby promoting transparency and accountability.
1.2 Regulatory Developments
The Capital Market Authority (CMA) has introduced corporate governance reforms to strengthen ESG considerations within the financial sector. These reforms aim to enhance the rights of shareholders and board members, ensuring that companies adhere to best practices in governance and sustainability.
Importance of Integrating ESG Factors into Risk Assessments
Incorporating ESG factors into risk assessments allows financial institutions to identify and mitigate potential risks that could impact their investments and operations. This approach not only safeguards financial performance but also contributes to sustainable development.
2.1 Environmental Risks
Environmental risks, such as climate change and resource depletion, can have significant financial implications. For example, companies with high carbon emissions may face regulatory penalties or reputational damage, affecting their profitability. By assessing environmental risks, financial institutions can make informed decisions that align with sustainability objectives.
2.2 Social Risks
Social risks encompass issues related to labor practices, community relations, and human rights. Companies that neglect social responsibilities may encounter operational disruptions or legal challenges. Integrating social factors into risk assessments helps identify potential vulnerabilities and promotes ethical business practices.
2.3 Governance Risks
Governance risks pertain to corporate governance structures, including board composition, transparency, and ethical conduct. Weak governance can lead to mismanagement and financial instability. Evaluating governance factors ensures that companies maintain robust oversight mechanisms, fostering investor confidence.
Current State of Sustainability and ESG Advisory in Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia has made significant strides in integrating ESG factors into its financial sector, yet challenges remain in achieving comprehensive adoption.
3.1 Progress Achieved
- ESG advisory Guidelines: Tadawul’s ESG advisory Guidelines have encouraged companies to report on their ESG performance, enhancing transparency and accountability.
- Green Investment Advisory Reforms: The CMA’s reforms have strengthened governance practices, aligning with international standards and promoting investor confidence.
- ESG Reporting and Disclosure Initiatives: Financial institutions, such as the Saudi National Bank (SNB), have developed sustainable finance frameworks to support projects that contribute to environmental and social objectives.
3.2 Challenges Faced
- Data Availability: The limited availability of reliable ESG data poses a challenge for accurate risk assessments. Companies may lack standardized reporting mechanisms, leading to inconsistencies.
- Awareness and Expertise: There is a need for increased awareness and expertise in ESG integration among financial professionals to effectively incorporate these factors into risk assessments.
- Regulatory Alignment: While progress has been made, further alignment of regulations with international ESG standards is necessary to ensure comprehensive adoption.
Quantitative Analysis of Sustainability and ESG Advisory in Saudi Arabia
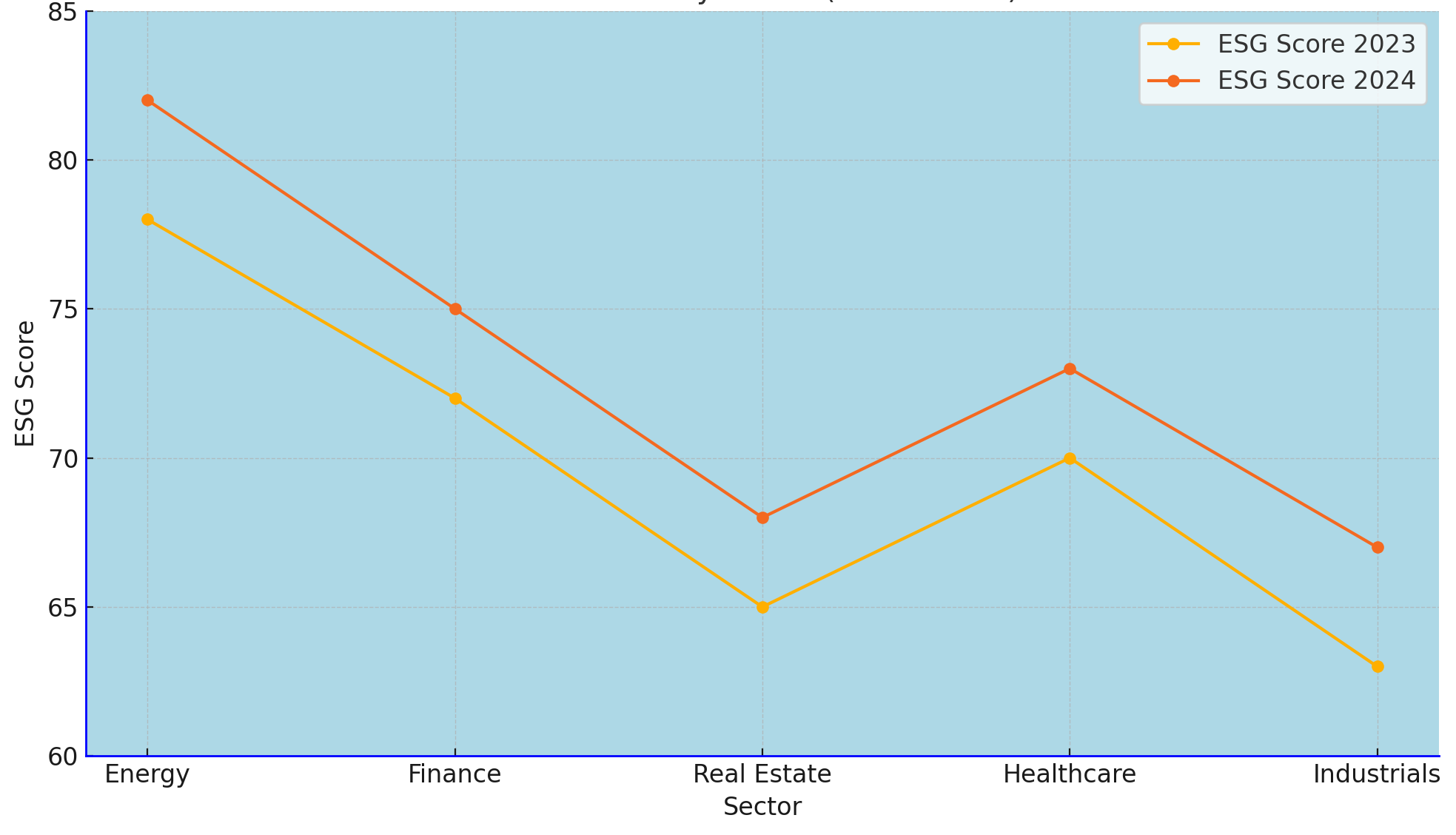
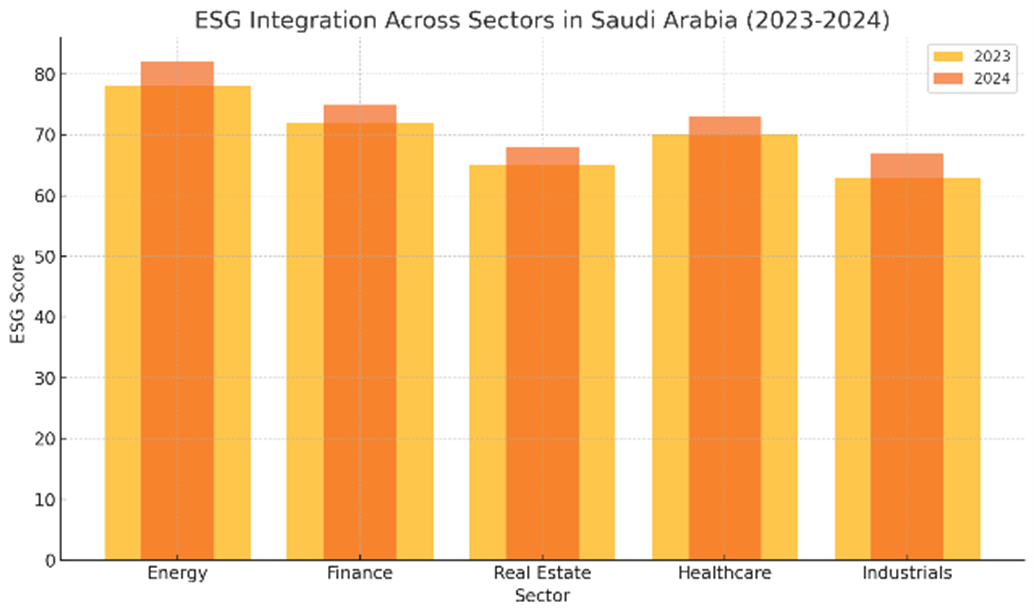
4.1 Data from key sectors highlights the growing focus on ESG integration:
4.2 Financial Performance: ESG vs. Non-ESG Companies
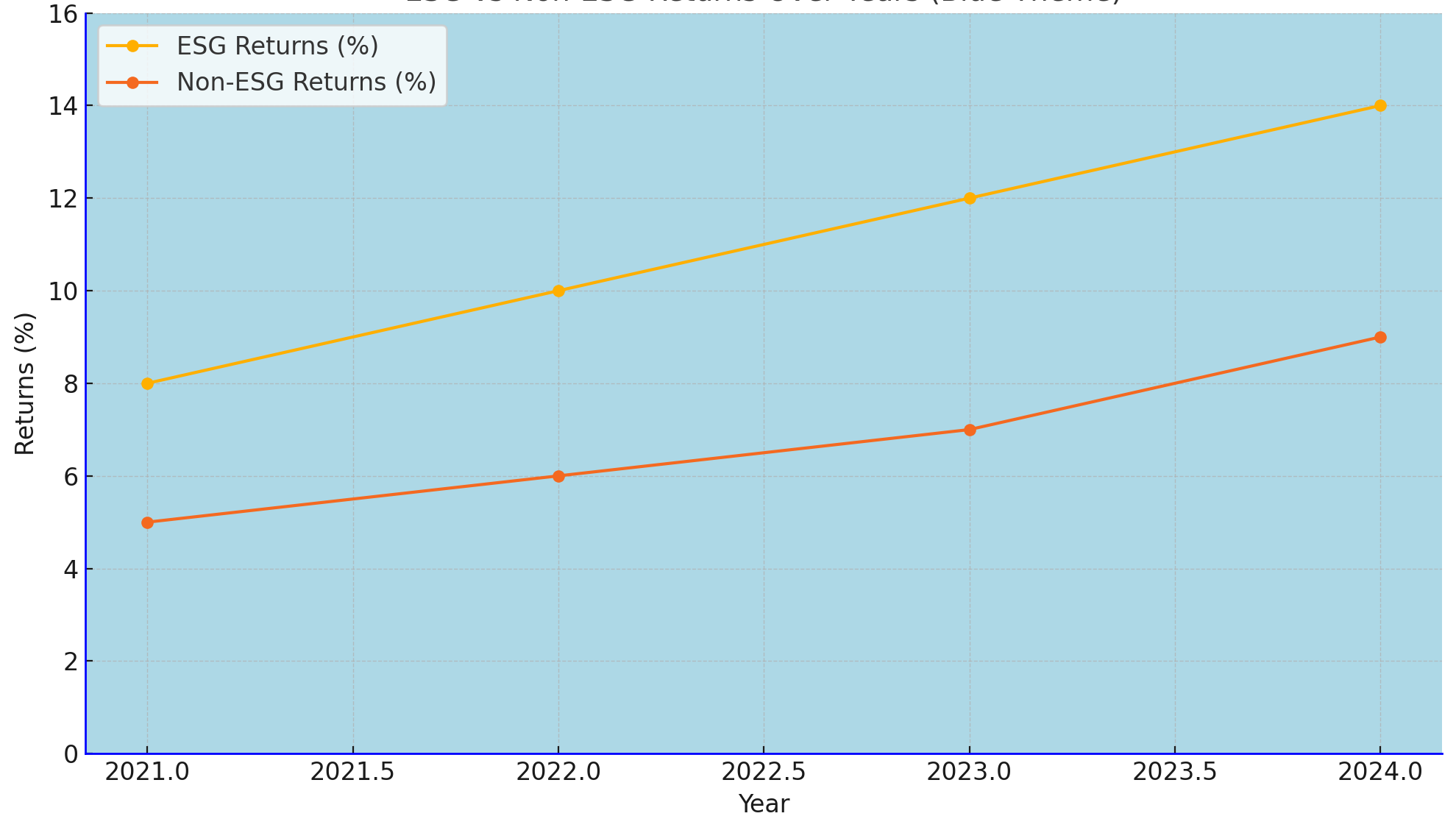
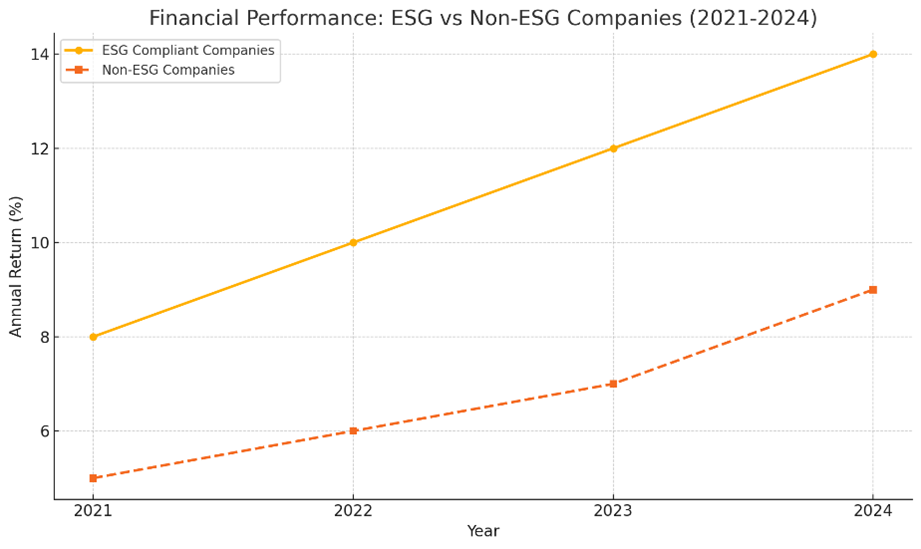
Analysis of annual returns indicates that ESG-compliant companies consistently outperform their non-ESG counterparts:
Visual Insights
Sustainability and ESG Advisory Across Sectors (2023-2024)
Financial Performance of ESG vs Non-ESG Companies (2021-2024)
Illustrates the superior returns of ESG-compliant companies.
Key Drivers of ESG Adoption in Saudi Arabia
The acceleration of ESG adoption in Saudi Arabia is fueled by a combination of regulatory mandates, market demand, and societal shifts.
5.1 Regulatory Influence
Saudi regulators are playing a critical role in advancing ESG adoption:
- Tadawul’s ESG advisory Guidelines: Encourage transparency in ESG reporting.
- Capital Market Authority (CMA): Implements corporate governance reforms to align with international ESG standards.
5.2 Market Demand
Investors are increasingly favoring ESG-compliant companies:
- Survey Insight: According to a 2024 KPMG report, 65% of institutional investors in the GCC region prioritize ESG factors when making investment decisions.
5.3 Societal Pressure
Consumers and stakeholders are pushing for more sustainable business practices:
- Statistic: A recent PwC survey revealed that 74% of Saudi consumers prefer products and services from companies with strong ESG commitments.
Comparative Analysis: Saudi Arabia vs. Global ESG Trends
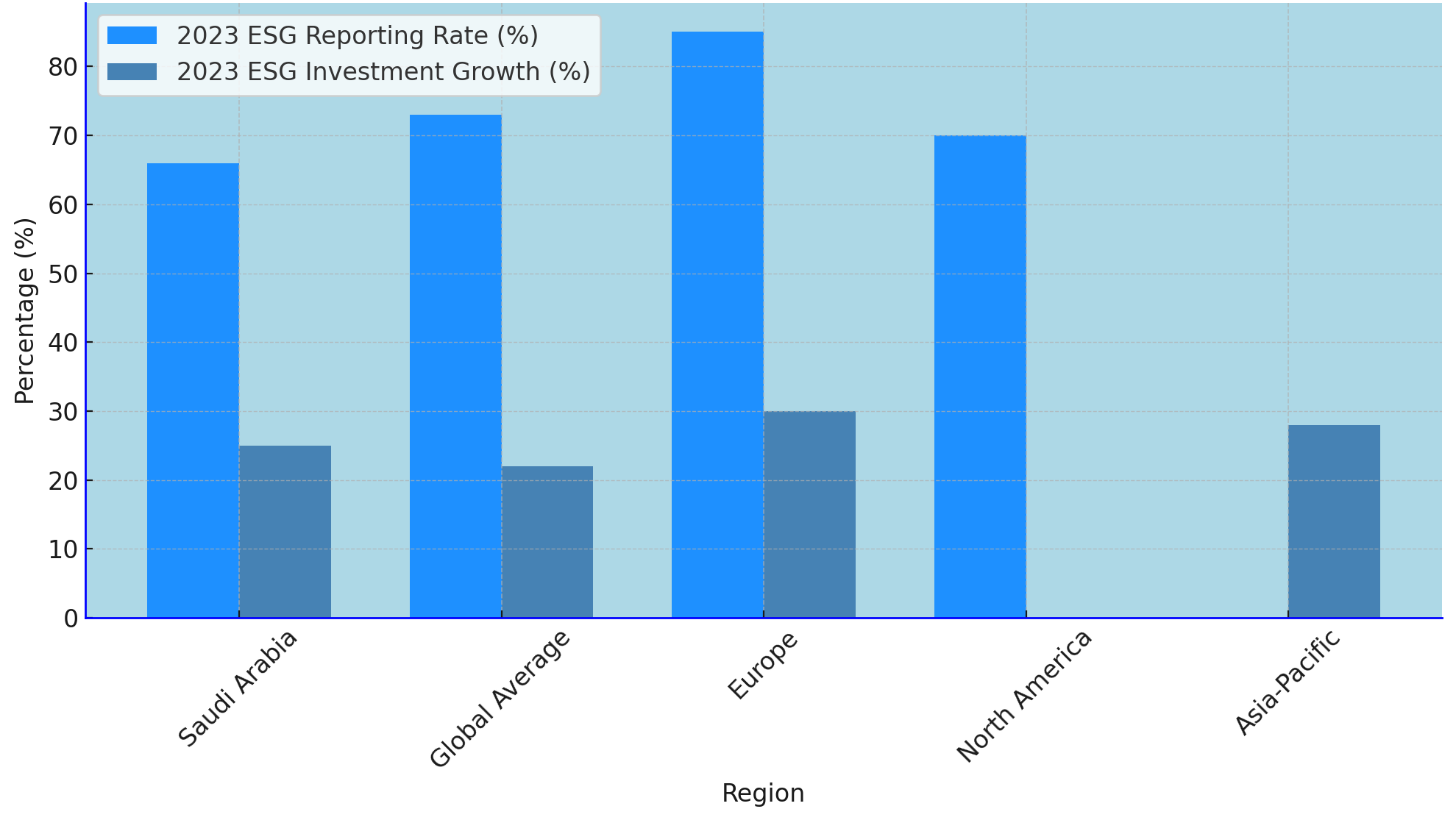
Insights Role in Shaping Saudi Arabia’s ESG Landscape
Insights play a pivotal role in advancing ESG integration within Saudi Arabia’s financial and corporate sectors. Leveraging cutting-edge technology, the firm provides real-time ESG data analytics, enabling organizations to make informed decisions and mitigate risks effectively. Insights collaborates closely with clients to develop comprehensive ESG frameworks ensuring compliance and enhancing transparency.
Through tailored training and development programs, Insights empowers organizations to build internal ESG capacity, fostering a culture of sustainability and responsible governance. Additionally, the firm offers detailed ESG performance benchmarking and reporting services, helping businesses meet regulatory expectations and investor demands. By adopting these tailored strategies, Insights enables organizations to position ESG as a core driver of innovation, resilience, and long-term growth in the evolving Saudi market.






