Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 is a transformative economic and social reform blueprint aimed at diversifying the Kingdom’s economy and reducing its dependency on oil revenues. The initiative focuses on creating a more vibrant society, thriving economy, and ambitious nation by leveraging non-oil sectors such as tourism, healthcare, and technology.
As with any transformative agenda, Vision 2030 comes with inherent risks, including economic, geopolitical, and regulatory uncertainties. Financial and Risk Advisory plays a crucial role in identifying, assessing, and mitigating these risks to ensure the success of this ambitious vision.
Key Objectives of Vision 2030
- Diversifying the Economy:
- Increase the contribution of non-oil sectors to GDP.
- Expand sectors like tourism, technology, and entertainment.
- Boosting Foreign Investment:
- Attract global investors to support mega-projects like NEOM, the Red Sea Project, and Qiddiya.
- Job Creation:
- Reduce the unemployment rate from 11.6% to 7% by 2030.
- Sustainability:
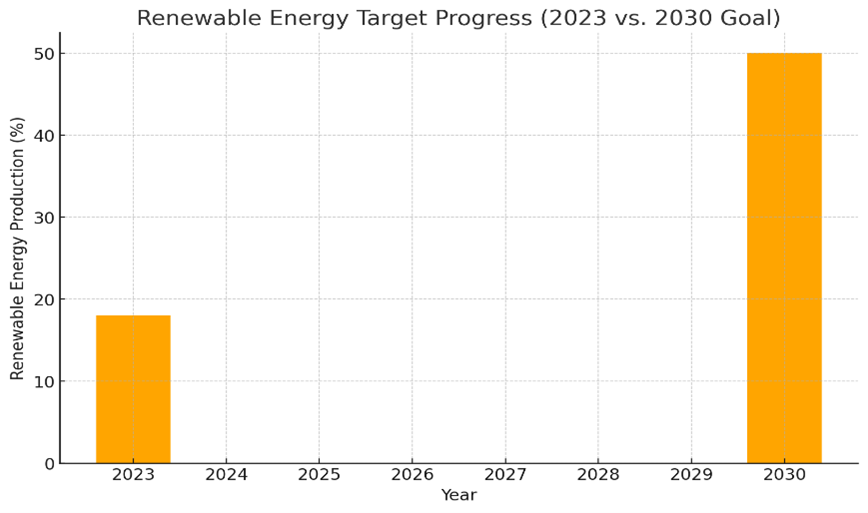
- Increase renewable energy production to 50% of total energy generation.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPP):
- Enhance collaboration between public and private sectors.
Opportunities in Risk Management
- Economic Diversification
Economic diversification opens new opportunities but brings risks associated with market volatility and competitive dynamics. Effective risk management enables policymakers to navigate these uncertainties.
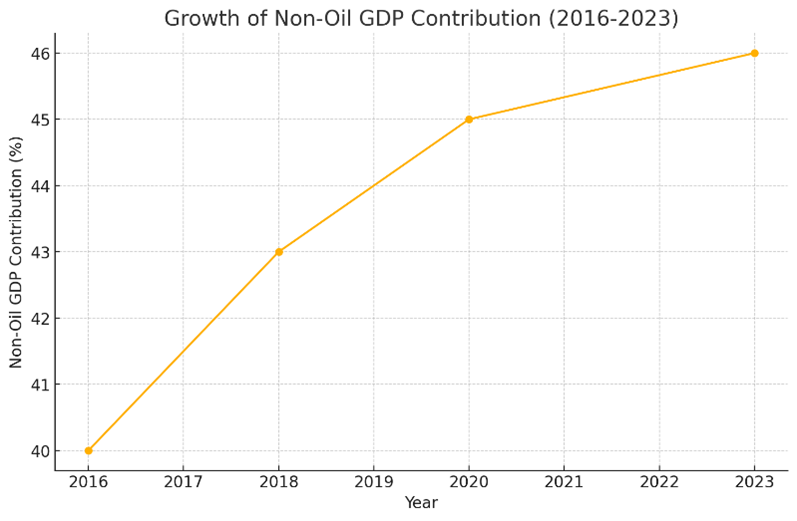
- Data Insight: The non-oil sector’s contribution to GDP has increased from 40% in 2016 to 46% in 2023. Vision 2030 aims to push this to over 60% by 2030.
Growth of Non-Oil GDP Contribution (2016-2023)
- Foreign Investment
Foreign investment is pivotal to financing Vision 2030 projects. By implementing a robust risk management framework, Saudi Arabia can attract and retain global investors.
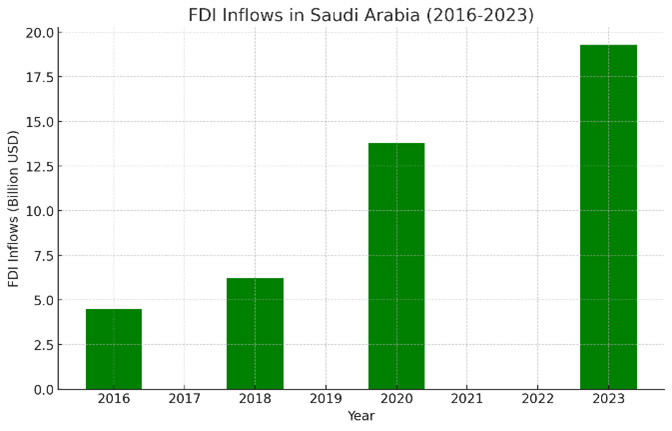
- Data Insight: FDI inflows have grown from $4.5 billion in 2016 to $19.3 billion in 2023, with a target of reaching $30 billion by 2030.
FDI Inflows in Saudi Arabia (2016-2023)
- Project Risk Management
Mega projects such as NEOM and The Red Sea Project involve high capital and long timelines, which increase risks related to delays and cost overruns.
Risk management in these projects involves:
- Monitoring project timelines.
- Mitigating financial risks through insurance.
- Regular risk assessments to ensure timely completion.
Challenges in Risk Management
- Regulatory Reforms
Rapid regulatory changes, while necessary, can create compliance risks for businesses. Companies must stay updated on new laws and ensure adherence to avoid penalties.
- Geopolitical Risks
Saudi Arabia is situated in a geopolitically sensitive region. Conflicts and diplomatic tensions can disrupt investment flows and trade, requiring agile risk management strategies.
- Technological and Cybersecurity Risks
As Saudi Arabia embraces digital transformation, it faces risks such as data breaches and cybersecurity threats. Establishing robust cybersecurity frameworks is essential to protect sensitive data.
- Climate and Sustainability Risks
Transitioning to renewable energy sources presents technical and financial risks. Additionally, extreme weather events pose risks to infrastructure projects.
Renewable Energy Target Progress (2023 vs. 2030 Goal)
Economic Risks and the Path to Diversification
Economic diversification is a critical goal under Vision 2030. Transitioning from an oil-dependent economy to one driven by sectors like technology, tourism, and entertainment introduces several economic risks. Market volatility in these emerging sectors poses a threat to stability, as their success often hinges on global demand and competition. Financial risks are also significant; expanding credit and investment in new industries increases exposure to defaults and capital misallocations. However, through comprehensive financial risk management, Saudi Arabia can safeguard its economic stability. Quantitative analysis reveals a positive trend, with non-oil GDP contributions rising steadily since 2016. To sustain this momentum, risk management must remain a priority.
Cybersecurity Risks in a Digitalized Economy
As Saudi Arabia embraces digital transformation, cybersecurity risks have become a critical concern. Initiatives like the National Digital Transformation Program aim to modernize public services and increase efficiency, but they also expose the Kingdom to cyber threats. Data breaches, ransomware attacks, and phishing schemes are increasingly sophisticated, posing significant risks to both public and private sectors. To combat these threats, Saudi Arabia has invested heavily in cybersecurity infrastructure, including the establishment of the National Cybersecurity Authority. Effective risk management in this domain involves continuous monitoring, threat detection, and the implementation of robust cybersecurity protocols.
How Technology is Transforming Risk Management in Saudi Arabia
The advent of advanced technologies has significantly enhanced risk management capabilities. In Saudi Arabia, the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in risk analysis has enabled more accurate risk predictions and faster response times. For example, AI can detect patterns in financial transactions to identify potential fraud, while ML algorithms can improve the accuracy of risk models over time. Additionally, blockchain technology is being utilized to enhance transparency and security in regulatory reporting. These technological innovations are not only transforming risk management practices but also providing a competitive edge to organizations that adopt them.
Insights on Navigating Future Risks
As Saudi Arabia progresses toward its Vision 2030 goals, new risks will inevitably emerge. These could include shifts in global economic conditions, technological disruptions, and evolving consumer preferences. Staying ahead of these risks requires continuous monitoring and a forward-looking approach. Insights into emerging risks enable policymakers and businesses to adapt their strategies proactively. Long-term risk planning, supported by data and technology, ensures that Saudi Arabia remains resilient and prepared for future challenges, securing its position as a global economic leader.
Quantitative Analysis
Let’s now look at some quantitative data to analyze the trends and impact of risk management in Vision 2030 initiatives.
| Indicator | 2016 | 2023 | 2030 Target |
| Non-Oil GDP Contribution (%) | 40% | 46% | 60% |
| FDI Inflows (Billion USD) | 4.5 | 19.3 | 30 |
| Renewable Energy Production (%) | 2% | 18% | 50% |
| Unemployment Rate (%) | 11.6% | 8.5% | 7% |
How Insights Can Help
- Advanced Risk Assessment Tools
Insights offer cutting-edge analytics platforms to identify and quantify risks, helping businesses and government entities make data-driven decisions.
- Training and Capacity Building
Through tailored training programs, Insights can enhance the risk management skills of teams across various sectors.
- Regulatory Compliance Support
As regulatory landscapes evolve, Insights provides guidance to navigate new laws, ensuring compliance and mitigating legal risks.
- Cybersecurity Solutions
Insights deliver robust cybersecurity frameworks to protect against data breaches and cyberattacks, ensuring secure operations in a digitalized economy.
- Sustainability Advisory
Insights help organizations integrate Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors into their risk management strategies, aligning with Vision 2030’s sustainability goals.






